Heat Exchangers
Aluminum Brazing SheetsFor Brazed Automobile Heat Exchangers

Cladding an aluminum-silicon alloy with a brazing sheet provides an aluminum alloy that has the thin walls necessary for use in automobile heat exchangers, as well as such desirable characteristics as high strength, corrosion resistance and formability. We have developed and are refining a variety of products of this sort.
Features
- We select from our diverse library of alloys the optimal combination of core materials and brazing materials that will suit the environment in which they will be used and the needs of each particular customer, and combine them into products.
- We develop highly reliable aluminum materials by determining the alloy's brazing material and cladding ratio, a diffuse interface due to the metallic composition of the core materials, and using flow control to form highly reliable joints.
- To ensure that heat exchangers have high corrosion resistance, we determine the brazing material's compatibility with the material to which it will be attached (fin materials or tube materials), decide on the alloy to be used as the core material, its metallic composition and optimal tempering.
- We provide products globally through our bases in Japan and overseas (China, Thailand and Greece).
Applications
- Automobile heat exchangers
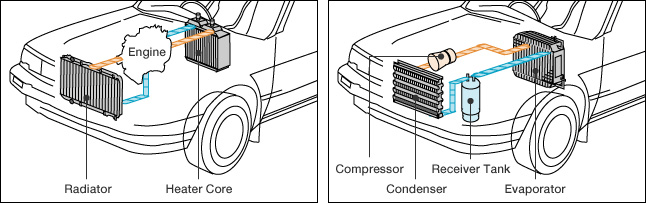
Types of heat exchangers
Product Characteristics
Characteristics Required for Brazing Sheets
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Ability of brazing material to adhere | Ability to form fillets in necessary locations |
| Corrosion resistance | No refrigerant or coolant tubing can pass through |
| Sag resistance | No high-temperature buckling during brazing |
| Strength | High strength, while more lightweight and with thinner walls |
| Heat transfer rate | Good heat conduction to disperse heat |
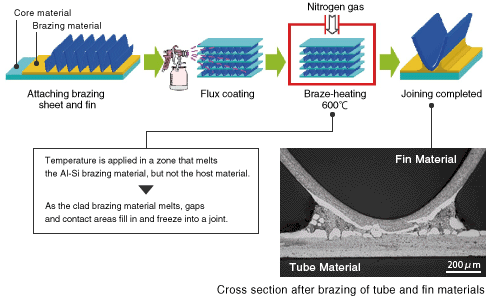
Fundamental Brazing Sheet Cladding Structure
Various types of brazing sheet used, depending on application
Single-sided cladding

Dual-sided cladding

Dual-sided cladding

Brazing material: Al-Si alloys, Core material: Al-Mn alloys, Sacrificial anode material: Al-Zn alloys, Plate thickness: 0.06–3.0 mm, Cladding ratio: 1–25%
Characteristics of cladding materials
Strength after brazing
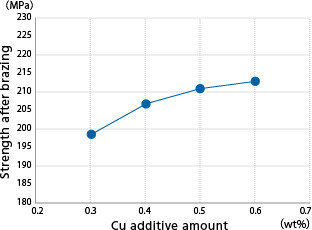
| Brazing material | Al-10Si |
|---|---|
| Core material | Al-Mn-Mg-Xcu |
| Brazing material | Al-10Si |
Plate thickness: 0.06–3.0 mm
Cladding ratio: 1–25%
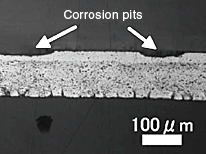
Cross sectional photo after corrosion testing
Overview of Brazing Material
Noncorrosive flux brazing method