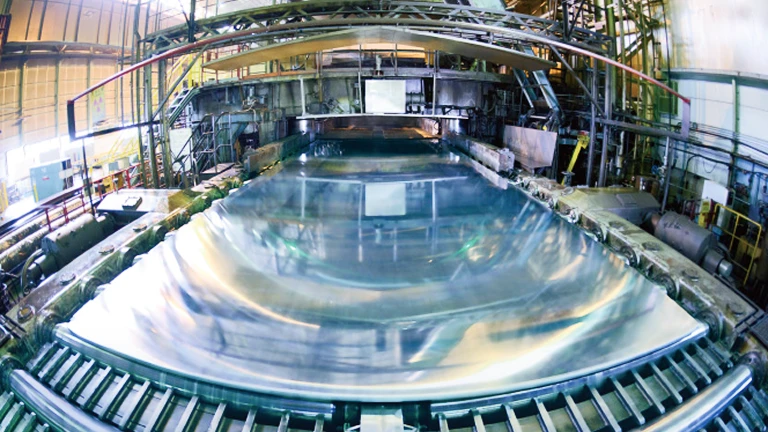
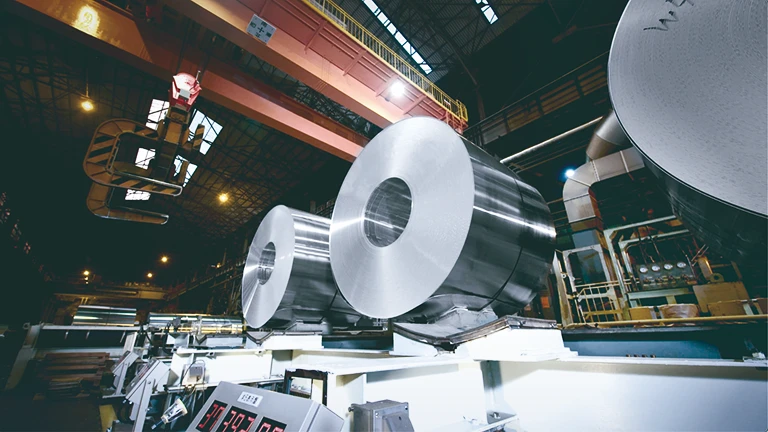
Pick Up


Promoting
aluminum recycling toward
a sustainable society
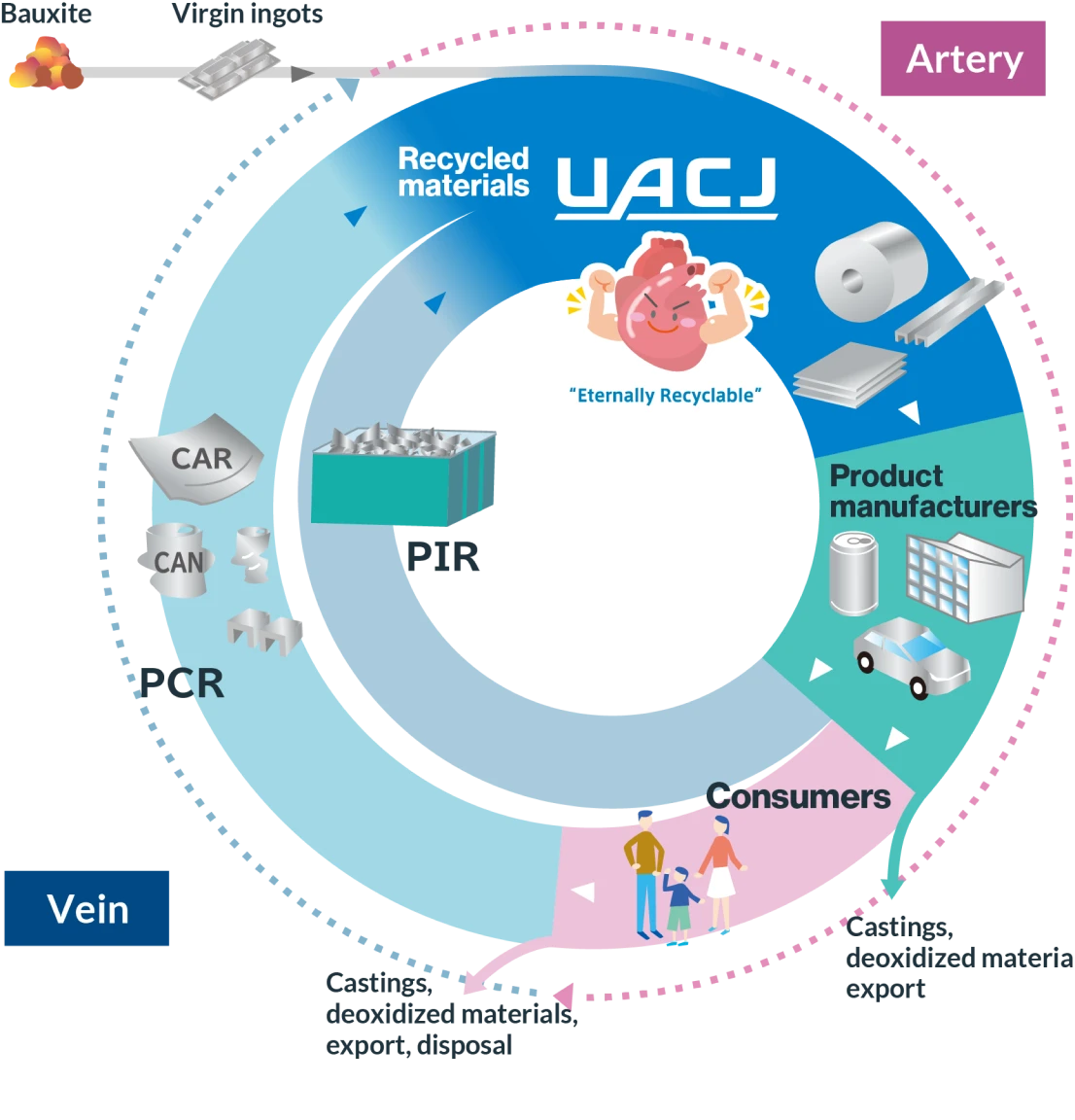
As a world-leading comprehensive aluminum manufacturer,
we serve as the "heart" of the aluminum recycling cycle,
contributing to industry development
and the realization of a sustainable society.


Important Notice




Information on Products and Technology
Technology and R&D
-

Here, we introduce the Group's philosophy, company profile, business summary, and domestic and overseas locations.
-

We also provide investor relations materials, growth strategies, financial data, and performance information, etc.
-

Here, we introduce our efforts toward the realization of a sustainable world.
Our Approach to Sustainability
A Future where the Earth can Continue to be Beautiful and Bountiful
A Healthy and Harmonious Society where Everyone can Feel Well-being